
-
 Mitchell leads Cavs over Pacers, Thunder beat 76ers
Mitchell leads Cavs over Pacers, Thunder beat 76ers
-
S. Korea's Yoon: from rising star to historic arrest

-
 Ominous Alcaraz sweeps into Australian Open third round
Ominous Alcaraz sweeps into Australian Open third round
-
'Queen Wen' deposed in huge shock at Australian Open

-
 Vigilante fire clean-up launched by local Los Angeles contractor
Vigilante fire clean-up launched by local Los Angeles contractor
-
Zheng dumped out in huge shock as shaky Sabalenka battles through

-
 Asian equities mixed as US inflation, China data loom
Asian equities mixed as US inflation, China data loom
-
'Queen Wen' Zheng deposed in huge shock at Australian Open

-
 Renewed US trade war threatens China's 'lifeline'
Renewed US trade war threatens China's 'lifeline'
-
China's economy seen slowing further in 2024: AFP survey

-
 Shaky Sabalenka overcomes serve struggles to stay alive in Melbourne
Shaky Sabalenka overcomes serve struggles to stay alive in Melbourne
-
South Korea's six weeks of political chaos

-
 Japan's tourism boom prices out business travellers
Japan's tourism boom prices out business travellers
-
What is the pink stuff coating fire-ravaged Los Angeles?

-
 Mediators make final push for Gaza truce deal
Mediators make final push for Gaza truce deal
-
Musk, Bezos, Zuckerberg to attend Trump inauguration: report

-
 Federal probe begins into deadly Los Angeles fires
Federal probe begins into deadly Los Angeles fires
-
'We may look easy-going, but...' Canadians veto Trump's merger plan

-
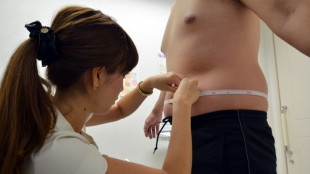 Is obesity a disease? Sometimes but not always, experts decide
Is obesity a disease? Sometimes but not always, experts decide
-
Biden issues land protections after LA fires delay ceremony

-
 Cuba to free over 550 prisoners after removal from US terror list
Cuba to free over 550 prisoners after removal from US terror list
-
Williams, Vine vie for season-opening Tour Down Under crown

-
 Maresca 'concerned' as Chelsea winless run stretches to five games
Maresca 'concerned' as Chelsea winless run stretches to five games
-
'Outstanding' Liverpool deserved more than Forest draw: Slot

-
 Guardiola laments Man City decision-making in Brentford collapse
Guardiola laments Man City decision-making in Brentford collapse
-
Marseille dumped out of French Cup on penalties

-
 Liverpool frustrated by Forest, Man City blow late lead at Brentford
Liverpool frustrated by Forest, Man City blow late lead at Brentford
-
Djokovic, Sabalenka chase history as Australian Open hits round two

-
 Golf star Woods pledges support amid 'unimaginable loss' of LA fires
Golf star Woods pledges support amid 'unimaginable loss' of LA fires
-
Liverpool held by Forest, Man City blow late lead at Brentford

-
 Cuba to free 553 prisoners after removal from US terror list
Cuba to free 553 prisoners after removal from US terror list
-
Leverkusen win to go one point behind Bayern, Kiel down Dortmund

-
 Jota rescues leaders Liverpool in Forest draw
Jota rescues leaders Liverpool in Forest draw
-
Title chasers Atalanta held by Juve, Milan hand Conceicao maiden Serie A win

-
 Man City blow late lead at Brentford, Chelsea held by Bournemouth
Man City blow late lead at Brentford, Chelsea held by Bournemouth
-
Rast charges through on second run to win Flachau slalom

-
 Grimaldo scores as Leverkusen go one point behind Bayern, Dortmund lose
Grimaldo scores as Leverkusen go one point behind Bayern, Dortmund lose
-
Starbucks shift on non-paying visitors stirs debate in US

-
 Clashes as S. Korean investigators attempt to arrest President Yoon
Clashes as S. Korean investigators attempt to arrest President Yoon
-
US, Japanese lunar landers set to launch on single rocket

-
 Boeing 2024 plane deliveries tumble on labor, safety woes
Boeing 2024 plane deliveries tumble on labor, safety woes
-
US removes Cuba from state sponsors of terror list

-
 Argentine annual inflation nosedives, in boost for Milei
Argentine annual inflation nosedives, in boost for Milei
-
S. Korea investigators arrive in new attempt to arrest President Yoon

-
 Pressure builds on Dortmund boss Sahin after loss at Kiel
Pressure builds on Dortmund boss Sahin after loss at Kiel
-
Meta to lay off 3,600 employees in performance-based cuts

-
 Venezuela restricts diplomats from 'hostile' European countries
Venezuela restricts diplomats from 'hostile' European countries
-
Trump's Pentagon pick grilled by senators as cabinet hearings begin

-
 From ban to buyout: What next for TikTok in the US?
From ban to buyout: What next for TikTok in the US?
-
Lazio sack doc who performed far-right falconer's penis op: club owner


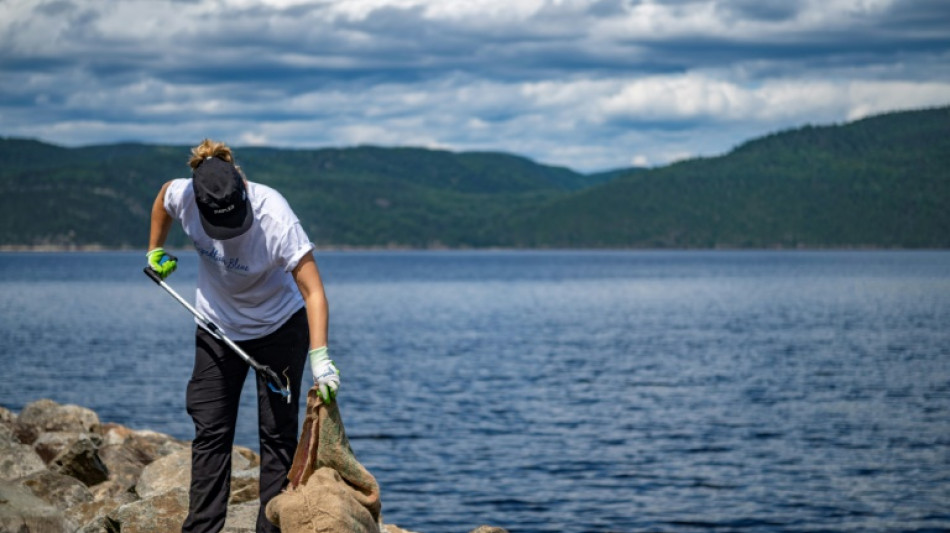
Scientists track plastic waste in pristine Canada marine park
Old tires, discarded cups, and cigarette butts litter the magnificent Saguenay Fjord, a marine protected area in eastern Canada that attracts belugas and other whales seeking respite.
Cliffs sculpted by glaciers flank the fjord that connects to the Saint Lawrence River, far from any major city. The marine sanctuary was granted protected status 26 years ago.
"It's one thing to legislate to make it a protected area, but then how do we maintain it?" said Canadian biologist Anne-Marie Asselin before diving in search of trash.
With her team from the Blue Organization, she navigates the brackish waters of the fjord to document pollution in the area.
The objective is twofold: to identify the most common waste to target the plastics that should be banned from sale, and to predict the banks most at risk of being polluted, based in particular on currents, to better target cleaning campaigns.
- Worrying trend -
By paddle board, on foot or freediving, Asselin and her crew collect all kinds of waste in the bay of the village of Petit-Saguenay.
Under a blazing hot sun, the group's Laurence Martel sorted the waste by more than 100 criteria, including by brand, to eventually seek to hold producers responsible for their products' entire lifecycle.
"The most popular find is the cigarette butt, it is omnipresent," Martel said.
She noted that a single cigarette butt can contaminate up to 500 liters of water due to the thousands of chemical compounds it contains.
In five years, the team's research has revealed a worrying trend: the concentration of plastic waste is increasing significantly closer to the Gulf of Saint Lawrence and the Atlantic, "suggesting a shift in waste from urban areas towards downstream parts of the river."
"Very often, the smallest plastics are the ones that pollute the most," Martel said.
- Ecosystem health -
Waste becomes microplastics as it disintegrates. Most often invisible to the naked eye, these particles are made of polymers and other toxic compounds that vary from five millimeters to one thousandth of a millimeter.
They are found throughout the food chain of marine life, particularly invertebrates.
The Blue Organization fishes and analyzes these "sentinel species" -- considered gauges of the health of their environment -- during each cleanup operation.
"If your mussels and your invertebrates are starting to suffer, that could be an indicator that the health of the ecosystem is also declining," said Miguel Felismino, of McGill University in Montreal.
Seated on a catamaran, Felismino measured, photographed and arranged the mussel specimens, which he will also analyze in a laboratory to study the effects of microplastics.
Using a homemade pump and a few pipes placed at the front of the boat, he also collected surface water and sediment from the seabed for his research
- Behavioral changes -
The Blue Organization wants to produce a complete picture of the plastic lifecycle in protected areas such as the Saguenay-Saint Lawrence Marine Park.
But to protect these ecosystems, the solution is "also to trigger behavioral changes" in people, said the biologist Asselin, who called on artists to "raise awareness" of the situation.
This could involve making music from natural sounds or creating a "literary translation" of scientific research, Asselin said.
"With climate change, the soundscapes associated with certain territories are set to evolve," said one such artist, Emilie Danylewick, before plunging her hydrophone into the water to record the sounds.
Danylewick said her work is a "way to preserve the current soundscape memory of the territory."
E.Schubert--BTB




