
-
 Stone tablet engraved with Ten Commandments sells for $5 million
Stone tablet engraved with Ten Commandments sells for $5 million
-
Perez leaves Red Bull after season of struggles

-
 First severe bird flu case in US sparks alarm
First severe bird flu case in US sparks alarm
-
UN experts urge three 'transformations' for nature

-
 Sergio Perez leaves Red Bull F1 team
Sergio Perez leaves Red Bull F1 team
-
13 dead after Indian navy speedboat rams ferry off Mumbai

-
 US Supreme Court agrees to hear TikTok ban case
US Supreme Court agrees to hear TikTok ban case
-
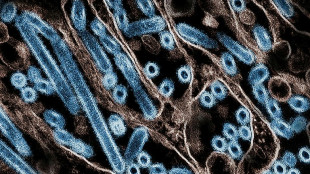
US reports first severe case of bird flu in a human
-
 Stocks and dollar edge higher before Fed rate decision
Stocks and dollar edge higher before Fed rate decision
-
UK PM Starmer wants football governance bill passed amid Super League talk

-
 France counts cyclone cost as aid reaches Mayotte
France counts cyclone cost as aid reaches Mayotte
-
'Lucky' Shiffrin in doubt for remainder of ski season

-
 Notre Dame cathedral unveils controversial new stained glass windows
Notre Dame cathedral unveils controversial new stained glass windows
-
Swiss club Young Boys name new coach in bid to stop slump

-
 UniCredit ups pressure on Commerzbank, fuelling German anger
UniCredit ups pressure on Commerzbank, fuelling German anger
-
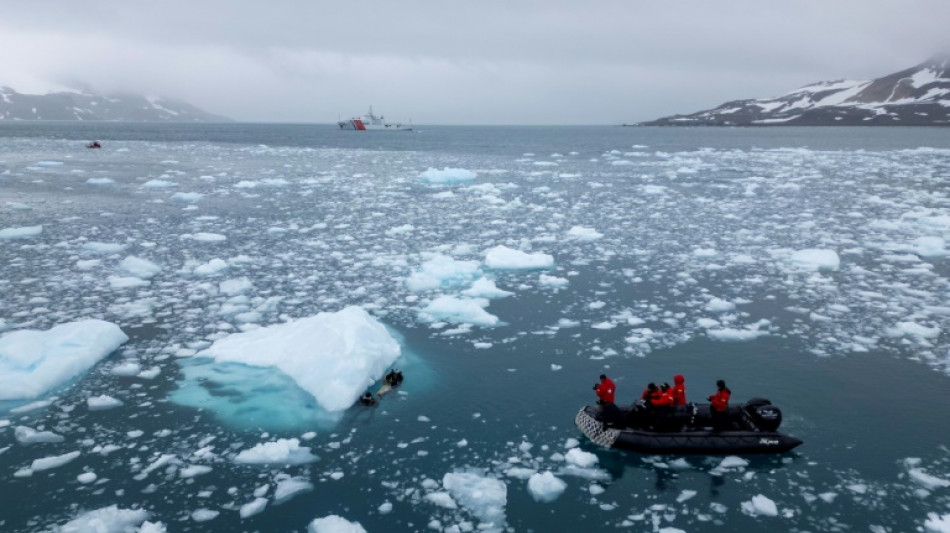
Melting sea ice in Antarctica causes ocean storms, scientists say

-
 Sarkozy must wear electronic tag after losing graft case appeal
Sarkozy must wear electronic tag after losing graft case appeal
-
Maresca insists Chelsea 'trust' Mudryk despite failed drugs test

-
 Stock steady, dollar climbs before Fed rate decision
Stock steady, dollar climbs before Fed rate decision
-
Spanish PM's wife denies wrongdoing in graft probe hearing

-
 'Ordinary and out of the ordinary': covering France's mass rape trial
'Ordinary and out of the ordinary': covering France's mass rape trial
-
Activist tells Saudi-hosted UN forum of 'silencing' of dissent

-
 UK electricity grid set for 'unprecedented' £35 bn investment
UK electricity grid set for 'unprecedented' £35 bn investment
-
Putin-tattooed dancer Polunin says leaving Russia

-
 USA star Weah picks up thigh injury: Juventus
USA star Weah picks up thigh injury: Juventus
-
France's Sarkozy must wear electronic tag after losing graft case appeal

-
 Olympic champion Hodgkinson's coaches eye 800m world record
Olympic champion Hodgkinson's coaches eye 800m world record
-
Germany criticises UniCredit's 'unfriendly' moves on Commerzbank

-
 Serbia's capital Belgrade to make public transport free
Serbia's capital Belgrade to make public transport free
-
Three 'transformations' for nature, according to UN experts

-
 Russian oil spill contaminates 50km of Black Sea beaches
Russian oil spill contaminates 50km of Black Sea beaches
-
Climate change made Cyclone Chido stronger: scientists

-
 After long delay, French nuclear plant coming on stream
After long delay, French nuclear plant coming on stream
-
Syrians face horror, fearing loved ones may be in mass graves

-
 UN calls for 'free and fair' elections in Syria
UN calls for 'free and fair' elections in Syria
-
Dutch authorities fine Netflix 4.75 mn euros over personal data use

-
 Further hike in UK inflation hits rate cut chance
Further hike in UK inflation hits rate cut chance
-
UK's Farage says in 'negotiations' with Musk over funding

-
 Fiji rules out alcohol poisoning in tourists' mystery illness
Fiji rules out alcohol poisoning in tourists' mystery illness
-
Pokemon is back with a hit new gaming app

-
 Flintoff to coach son on England second-string tour of Australia
Flintoff to coach son on England second-string tour of Australia
-
Stock markets, dollar climb before Fed rate decision

-
 Spain PM's wife testifies in corruption case
Spain PM's wife testifies in corruption case
-
Belgian cycling legend Rik Van Looy dies aged 90

-
 Syria's first flight since Assad's fall takes off
Syria's first flight since Assad's fall takes off
-
Devastated Mayotte battles to recover from cyclone 'steamroller'

-
 France assesses scale of Mayotte 'disaster' as aid arrives
France assesses scale of Mayotte 'disaster' as aid arrives
-
US, Chinese ships at Cambodia bases as Washington navigates diplomatic currents

-
 Amorim eager for wantaway Rashford to stay at Manchester United
Amorim eager for wantaway Rashford to stay at Manchester United
-
Warmer winter melts incomes of China's ice cutters


Melting sea ice in Antarctica causes ocean storms, scientists say
The record-breaking retreat of Antarctic sea ice in 2023 has led to more frequent storms over newly exposed parts of the Southern Ocean, according to a study published Wednesday.
Scientists know that the loss of Antarctic sea ice can diminish penguin numbers, cause ice shelves to melt in warmer waters, and impede the Southern Ocean from absorbing carbon dioxide.
But this new research, published in the peer-reviewed journal Nature, explores another consequence: increased heat loss from the ocean to the atmosphere, and an associated rise in storms.
Since 2016 there has been a large-scale reduction in Antarctic sea ice, but nothing like 2023 when a record amount failed to reform over the winter.
For this study, Simon Josey of the UK's National Oceanography Centre and colleagues focussed on three regions that experienced unusually high levels of sea-ice retreat that year.
Using satellite imagery, ocean and atmospheric data, and wind and temperature measurements, they found some newly ice-free areas experienced double the heat loss compared to a stabler period before 2015.
This was accompanied by "increases in atmospheric-storm frequency" over previously ice-covered regions, the authors found.
"In the sea-ice-decline regions, the June–July storm frequency has increased by up to 7 days per month in 2023 relative to 1990–2015."
The loss of heat caused by reduced sea ice could have implications for how the ocean circulates and the wider climate system, the study added.
Oceans are a crucial climate regulator and carbon sink, storing more than 90 percent of the excess heat trapped near Earth's surface by greenhouse gas emissions.
In particular, sea-ice retreat could mean changes in how a deeper layer of cold, dense Antarctic bottom water absorbs and stores heat.
The authors said further in-depth analysis of possible climate impacts were needed, including if sea-ice retreat could have even further-reaching consequences.
"Repeated low ice-cover conditions in subsequent winters will strengthen these impacts and are also likely to lead to profound changes further afield, including the tropics and the Northern Hemisphere," it said.
N.Fournier--BTB



