-
 Palestinians welcome ICC arrest warrants for Israeli officials
Palestinians welcome ICC arrest warrants for Israeli officials
-
Senegal ruling party wins parliamentary majority: provisional results

-
 Fiji's Loganimasi in for banned Radradra against Ireland
Fiji's Loganimasi in for banned Radradra against Ireland
-
New proposal awaited in Baku on climate finance deal

-
 Brazil police urge Bolsonaro's indictment for 2022 'coup' plot
Brazil police urge Bolsonaro's indictment for 2022 'coup' plot
-
NFL issues security alert to teams about home burglaries

-
 Common water disinfectant creates potentially toxic byproduct: study
Common water disinfectant creates potentially toxic byproduct: study
-
Chimps are upping their tool game, says study

-
 US actor Smollett's conviction for staged attack overturned
US actor Smollett's conviction for staged attack overturned
-
Fears rise of gender setbacks in global climate battle

-
 'World's best coach' Gatland 'won't leave Wales' - Howley
'World's best coach' Gatland 'won't leave Wales' - Howley
-
Indian PM Modi highlights interest in Guyana's oil

-
 Israel strikes kill 22 in Lebanon as Hezbollah targets south Israel
Israel strikes kill 22 in Lebanon as Hezbollah targets south Israel
-
Argentina lead Davis Cup holders Italy

-
 West Bank city buries three Palestinians killed in Israeli raids
West Bank city buries three Palestinians killed in Israeli raids
-
Fairuz, musical icon of war-torn Lebanon, turns 90

-
 Jones says Scotland need to beat Australia 'to be taken seriously'
Jones says Scotland need to beat Australia 'to be taken seriously'
-
Stock markets push higher but Ukraine tensions urge caution

-
 IMF sees 'limited' impact of floods on Spain GDP growth
IMF sees 'limited' impact of floods on Spain GDP growth
-
Fresh Iran censure looms large over UN nuclear meeting

-
 Volkswagen workers head towards strikes from December
Volkswagen workers head towards strikes from December
-
'More cautious' Dupont covers up in heavy Parisian snow before Argentina Test

-
 UK sanctions Angola's Isabel dos Santos in graft crackdown
UK sanctions Angola's Isabel dos Santos in graft crackdown
-
Sales of existing US homes rise in October

-
 Crunch time: What still needs to be hammered out at COP29?
Crunch time: What still needs to be hammered out at COP29?
-
Minister among 12 held over Serbia station collapse

-
 Spurs boss Postecoglou hails 'outstanding' Bentancur despite Son slur
Spurs boss Postecoglou hails 'outstanding' Bentancur despite Son slur
-
South Sudan rejects 'malicious' report on Kiir family businesses

-
 Kyiv claims 'crazy' Russia fired nuke-capable missile
Kyiv claims 'crazy' Russia fired nuke-capable missile
-
Australia defeat USA to reach Davis Cup semis

-
 Spain holds 1st talks with Palestinian govt since recognising state
Spain holds 1st talks with Palestinian govt since recognising state
-
Stock markets waver as Nvidia, Ukraine tensions urge caution

-
 Returning Vonn targets St Moritz World Cup races
Returning Vonn targets St Moritz World Cup races
-
Ramos nears PSG return as Sampaoli makes Rennes bow

-
 Farrell hands Prendergast first Ireland start for Fiji Test
Farrell hands Prendergast first Ireland start for Fiji Test
-
Gaza strikes kill dozens as ICC issues Netanyahu arrest warrant

-
 Famed Berlin theatre says cuts will sink it
Famed Berlin theatre says cuts will sink it
-
Stuttgart's Undav set to miss rest of year with hamstring injury

-
 Cane, Perenara to make All Blacks farewells against Italy
Cane, Perenara to make All Blacks farewells against Italy
-
Kenya scraps Adani deals as Ruto attempts to reset presidency

-
 French YouTuber takes on manga after conquering Everest
French YouTuber takes on manga after conquering Everest
-
Special reunion in store for France's Flament against 'hot-blooded' Argentina

-
 'World of Warcraft' still going strong as it celebrates 20 years
'World of Warcraft' still going strong as it celebrates 20 years
-
Fritz pulls USA level with Australia in Davis Cup quarters

-
 New Iran censure looms large over UN nuclear meeting
New Iran censure looms large over UN nuclear meeting
-
The first 'zoomed-in' image of a star outside our galaxy

-
 ICC issues arrest warrants for Netanyahu, Gallant, Deif
ICC issues arrest warrants for Netanyahu, Gallant, Deif
-
Minister among 11 held over Serbia station collapse

-
 Historic gold regalia returned to Ghana's king
Historic gold regalia returned to Ghana's king
-
Kyiv accuses Russia of launching intercontinental ballistic missile attack


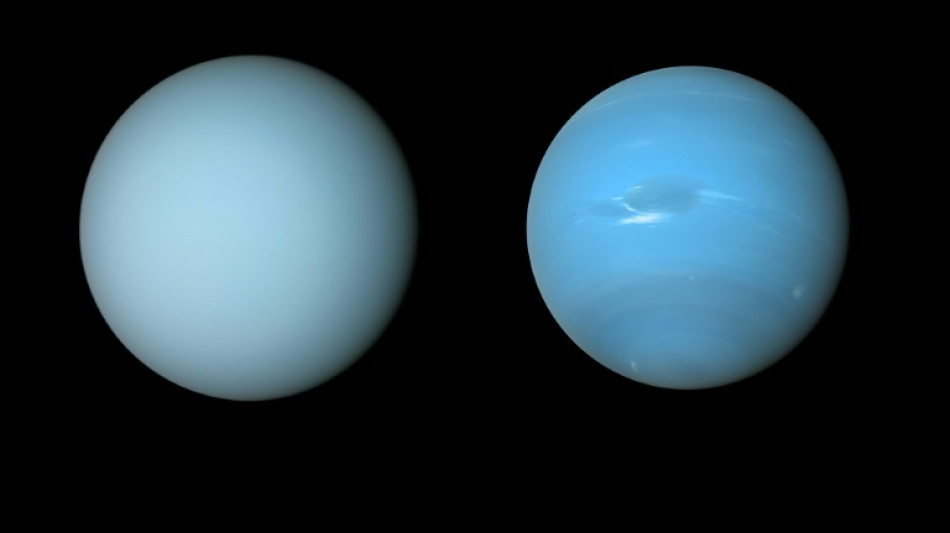
It's raining diamonds across the universe, research suggests
It could be raining diamonds on planets throughout the universe, scientists suggested Friday, after using common plastic to recreate the strange precipitation believed to form deep inside Uranus and Neptune.
Scientists had previously theorised that extremely high pressure and temperatures turn hydrogen and carbon into solid diamonds thousands of kilometres below the surface of the ice giants.
Now new research, published in Science Advances, inserted oxygen into the mix, finding that "diamond rain" could be more common than thought.
Ice giants like Neptune and Uranus are thought to be the most common form of planet outside our Solar System, which means diamond rain could be occurring across the universe.
Dominik Kraus, a physicist at Germany's HZDR research lab and one of the study's authors, said that diamond precipitation was quite different to rain on Earth.
Under the surface of the planets is believed to be a "hot, dense liquid", where the diamonds form and slowly sink down to the rocky, potentially Earth-size cores more than 10,000 kilometres (6,200 miles) below, he said.
There fallen diamonds could form vast layers that span "hundreds of kilometres or even more", Kraus told AFP.
While these diamonds might not be shiny and cut like a "a nice gem on a ring", he said they were formed via similar forces as on Earth.
Aiming to replicate the process, the research team found the necessary mix of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen in a readily available source -- PET plastic, which is used for everyday food packaging and bottles.
Kraus said that while the researchers used very clean PET plastic, "in principle the experiment should work with Coca-Cola bottles".
The team then turned a high-powered optical laser on the plastic at the SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory in California.
"Very, very short X-ray flashes of incredible brightness" allowed them to watch the process of nanodiamonds -- tiny diamonds too small to see with the naked eye -- as they formed, Kraus said.
"The oxygen that is present in large amounts on those planets really helps suck away the hydrogen atoms from the carbon, so it's actually easier for those diamonds to form," he added.
- New way to make nanodiamonds? -
The experiment could point towards a new way to produce nanodiamonds, which have a wide and increasing range of applications including drug delivery, medical censors, non-invasive surgery and quantum electronics.
"The way nanodiamonds are currently made is by taking a bunch of carbon or diamond and blowing it up with explosives," said SLAC scientist and study co-author Benjamin Ofori-Okai.
"Laser production could offer a cleaner and more easily controlled method to produce nanodiamonds," he added.
The diamond rain research remains hypothetical because little is known about Uranus and Neptune, the most distant planets in our Solar System.
Only one spacecraft -- NASA's Voyager 2 in the 1980s -- has flown past the two ice giants, and the data it sent back is still being used in research.
But a NASA group has outlined a potential new mission to the planets, possibly launching next decade.
"That would be fantastic," Kraus said.
He said he is greatly looking forward to more data -- even if it takes a decade or two.
F.Pavlenko--BTB

